My Starship Construction in the Frontier post generated a lot of discussion in the Star Frontiers group on Facebook. In some of the discussion, the commenters seemed to be making the assumption that I wanted to increase the number of ships flying around and that my post was advocating for ways to do that. I actually don’t have a strong feeling one way or another. In fact, I’m much more in the camp of small numbers of ships.
What I’m really looking at, and am interested in figuring out, are the implications those small numbers have and whether or not it makes sense to increase the numbers. Or if you don’t, what that implies for the realities of life in the Frontier and how that impacts the player characters.
I’m interested in questions like, if you only have a small number of ships across the Frontier, what does that mean for interstellar commerce? What impacts does that have on interstellar travel? Who owns the ships? What do they cost? And questions like that.
Since that starship construction article came out, and the ensuing discussion, I’ve been thinking more and more about this and have decided to do a series of articles on the topic. They will all have the Economics of Spaceflight title and a similar tag. In this first article, I’m going to look at interstellar passenger travel.
From the Rules
Let’s start by looking at what the rules say about these ships, which it calls starliners, and interstellar travel. We’ll begin with the description given on page 6 of the Knight Hawks Campaign Book:
Spaceliners. HULL SIZE = 6-15. Spaceliners (passenger transports) are built in a wide variety of sizes. Modern spaceliners are fast, quiet ships, capable of providing the wealthy passenger with any conceivable luxury. Many of the older liners are smaller, somewhat decrepit vessels that promise only the fundamental requirements of life support. The number of passengers carried by a spaceliner is about 25 times the ship’s hull size. For example, a spaceliner with a hull size of 10 can carry 250 passengers. Engine durability varies as much as size on spaceliners. Some will require an overhaul after three jumps, while others will be able to make 8 or 10 interstellar trips without maintenance.
KH Campaign Book, p. 6
This gives us a bit of information right off the bat. First, we have the range of hull sizes for these types of ships and the number of passengers per hull size. I’ll have more to say on that latter concept later. It also seems to imply that there are a bunch of these flying around as it describes various generations of ships. Other bits, such as the comments on engine overhauls, tell us that they typically sport atomic engines (as ion drives don’t need overhauls) and indicate some of the properties of the Class B and C atomic engines which the rules haven’t covered yet if you’re just reading through the book.
In the original Alpha Dawn Expanded Rules book, pages 49 and 50 talk about they modes and costs of interstellar travel. It lists three “classes” of travel accommodations and their costs:
- First Class – luxurious accommodations with the best rooms, food, and and best access to survival gear in the case of an emergency. 200 Credits per light year traveled.
- Journey Class – This is the standard accommodations. 100 Credits per light year traveled.
- Storage Class – In this class, you travel as frozen cargo. 30 Credits per light year traveled.
More details on the accommodation types are given on page 21 of the Knight Hawks Campaign Book.
Travel time is one of the areas where the Alpha Dawn (AD) and Knight Hawks (KH) rule sets conflict with one another. The AD rules say that interstellar travel occurs at the rate of one day per light year, while the KH rules, require 10 hours (one day’s work) per light year to plot out the jump, but actually making the jump takes 8.7 days regardless of the distance. Reconciling and clearing that up is a whole article in and of itself. We’ll save that for a future date. For this article, we’re going to assume that it takes 9 days to make a jump, regardless of the distance.
Of course that probably means the cost of a ticket should be fixed as the same number of resources go into making a jump regardless of the distance but for now we’ll go with the AD rules ticket costs.
If the PCs come into possession of a starliner, either via salvage, original constructions, or some other means, the KH Campaign Book (p. 44) provides guidance on what it costs to operate such a ship, how much of the ship is full on any given trip, and the risks involved. We’ll come back to those numbers later as well.
How Many Passengers – revisited
For this article, we’re going to be looking at a HS 10 passenger liner which falls in the middle of the range specified in the KH rules. According to the rules, this ship can carry 250 passengers. The question is, does this make sense?

Let’s look at some sources. A HS 10 ship is roughly the size of a modern, large cruise ship here on Earth. These ships typically hold up to 2800 passengers and 1200 crew, for a total of 4000 people, or 400 per hull size. But that’s the maximum capacity and typically means 4 people to a cabin. If you’ve ever been on a cruise ship, you know those cabins are small, typically 15-22 square meters. Now this is roughly the size of a Journey Class cabin on our starliner (16-24 square meters), the difference being that that size on our starliner is for a single being, not a group of four. That immediately means we need to cut our passenger estimate down by a factor of four putting us at about 700 passengers.
The other thing our starliner has to deal with, that a cruise ship doesn’t, it life support. On a cruise ship, air is free. And while there is probably some recycling of water, it’s not a closed loop with full filtering needed. And cruise ships tend to stop and replenish supplies every couple of days unless it’s a long trans-oceanic cruise. So they don’t carry a lot of food on board. In the Frontier, ships are typically designed to carry half a year of food and the systems to process the air, water, and waste onboard which eats up more space on the ship.
Then you have all the lifeboats, spacesuits, and other ship’s vehicles that our starliner has to have. Cruise ships have lifeboats but the passenger density on them is going to be higher than the ones on our starliner and the some of the lifeboats on cruise ships are inflatable. That’s not going to happen on a starship. Those eat up space as well.
Finally, a cruise ship has a lot of the upper decks exposed to air. That doesn’t count against it’s volume but provides a lot of communal space for the passengers. That space needs to exist on starliners as well but has to be enclosed within the hull.
Between the extra life support machinery, the communal space, and the ship’s vehicles, that could easily reduce the capacity of the ship by 30 to 70 percent depending on how you figure it. 250 passengers is just 36% of the 700 passenger number we had left above. It’s possibly at the low end, but reasonable.
Another point of comparison is the volume based rules I created for starship generation. In that system, which accounts for passageway, cabin space, and storage space, I designed a ship the same size as a HS 10 ship in the KH rules. It had a total of 100 First Class cabins, 1250 Journey class cabins, and 200 Storage class cabins. And that includes the cabins for the crew, the size of which the rules don’t address. For this I’ll assumed 50 of the Journey class cabins are for the (lots of robots on Frontier ships). So the total capacity is 1500 passengers, which is a little large. However, this system doesn’t currently account for communal space which could easily be as much or more than the space taken up by the cabins. So if we cut that number in half we’re back to 750 passengers, similar to our initial estimate from the cruise ship.
The bottom line is that while 250 is probably a bit low, it’s not unreasonable and the actual number might be only a factor of 2 or 3 higher. So we’ll go with 250 passengers for our analysis.
A Typical Journey
The Starliner
Okay, we have our ship, it carries 250 passengers. What does a typical journey look like? For this example, we’re going say this ship makes the run between Gran Quivera in the Prenglar system and Triad in the Cassidine system, a jump of 7 light years. We’ll look at the finances later, right now we are going to just look at logistics.
We’ll start the journey at the point when the ship is all loaded and ready to depart Gran Quivera for Triad. The first step is the jump to the Cassidine system. It takes just under 4.5 days to get to jump speed and the same amount of time to slow down. We’ll assume the total travel time is 9 days. In truth it could be up to 11 days depending on the orbital dynamics of the two systems and how accurate the jump is but we’ll go with 9 days.
After docking at the station around Triad, the ship has to do a number of housekeeping activities. First, the passengers have to disembark, then the interior of the ship needs to be cleaned. And new provisions need to be taken aboard. Then the passengers and the luggage for the next trip need to board.
Since this is a HS 10 ship, it has three Class B atomic engines. These engines require an overhaul after every three jumps. Since there are three engines, it makes sense to stagger the overhauls so that you do one after each jump. You’re always doing an overhaul each time in port, but you are only doing one and that make it reasonable. We’ll also top off the fuel pellets in the engine we’re doing the overhaul on. We’ll assume that the ship has two level 4 engineers on board that work alternating shifts so that maintenance and overhaul work can proceed around the clock to be as efficient as possible.
Let’s look at time scales. If a cruise ship can load or unload it’s 2800 passengers in a single day, I think it’s safe to assume that our 250 passengers can be loaded and unloaded in a single day as well. So that requires two days in port for those two operations. Refueling one engine takes on average 7 hours. The engine overhaul takes on average 38 hours. That’s a total of 45 hours of work. Assuming it is split between the two engineers, either working together on 10 hour shifts or around the clock on alternating shifts, that takes two and a quarter days. We’ll call it three to account for any variations and potential issues that come up. The provisioning and cleaning can occur while the engine work is happening. So our ship spends 5 days in port and then is ready for the return journey to Gran Quivera. So far we’re up to 14 days.
The trip back is exactly the same. It takes 9 days to make the jump, and another 5 days in port before it’s ready to leave. That is a total round trip time of 28 days.
The Shuttle
That’s the main part of the journey. You also need some way to get the passengers from the surface of the planet up to the station to board the starliner. That means you’re going to need a shuttle. For comparison, a Boeing 737 is about the size of a HS 2 ship. And it carries 175 people and their luggage. A Boeing 747 is about the size of a HS 3 ship and it carries 416 people plus luggage.
Now the trip up to the ship isn’t that long. As the Dutch astronaut Wubbo Ockels commented about his 1985 trip on the Space Shuttle Challenger:
Space is so close: It took only eight minutes to get there and twenty to get back.
That was at 3g and we probably want to be a little gentler on our passenger but it shouldn’t take more than a half hour to get into orbit and an hour back. They will need acceleration couches regardless and those take up a bit more room than a typical airline seat but not by much. It’s completely reasonable that a HS 3 shuttle can carry the 250 passengers for our space liner.
That means that we’ll need one shuttle at each system. If we let our spaceliner carry more than the 250 passengers, we’ll need more shuttles as well.
How Many Ships Do We Need?
With one ship, every 28 days we can move 250 beings from Gran Quivera to Triad and another 250 beings in the reverse direction. If this is the only ship running the route, there will only be a single trip once a month between the worlds. If you miss your flight, you’ll have to wait 28 days for the ship to be back. And if you want a round trip then you will spend at least 5 days in the destination system assuming you fly back out immediately when the ship leaves, otherwise it will be 33 days (or longer) after you arrive before you can catch a ship back.
Of course we can increase the frequency by adding more ships on the route. Let’s say we want a flight leaving every day. That’s easy enough. It’s a 28 day round trip for a single ship, you just need 28 ships and means you have a departure and arrival every day. And that allows you to move 250×28 or 7000 beings each way between the two systems in that same 28 day time period.
Regardless of how often you have interstellar departures (as long as it’s not more than once a day), your one shuttle can supply all of those ships. So even though you have 28 starliners, you only need a single shuttle at each system to handle the passenger traffic.
But that’s not the whole story. Each of those ships needs to have annual maintenance performed and that will take on average 15-16 days per ship. Which means once a year, each ships needs to be pulled out of rotation for one cycle to have it’s maintenance done. That means we need a spare ship to fill in while it’s out of commission. If you’re running a ship every day, you’ll actually need two spare ships to cover the gaps as the repair time on 28 ships is longer than a year and there will be some times when two ships are in maintenance. The shuttle needs annual maintenance as well, but that only takes on average 8-9 days as it is a smaller ship. If you only have 1-3 flights in that 28 day period, you can get away with a single shuttle and squeeze in its maintenance between runs, otherwise, you’ll need two of them to cover the maintenance periods.
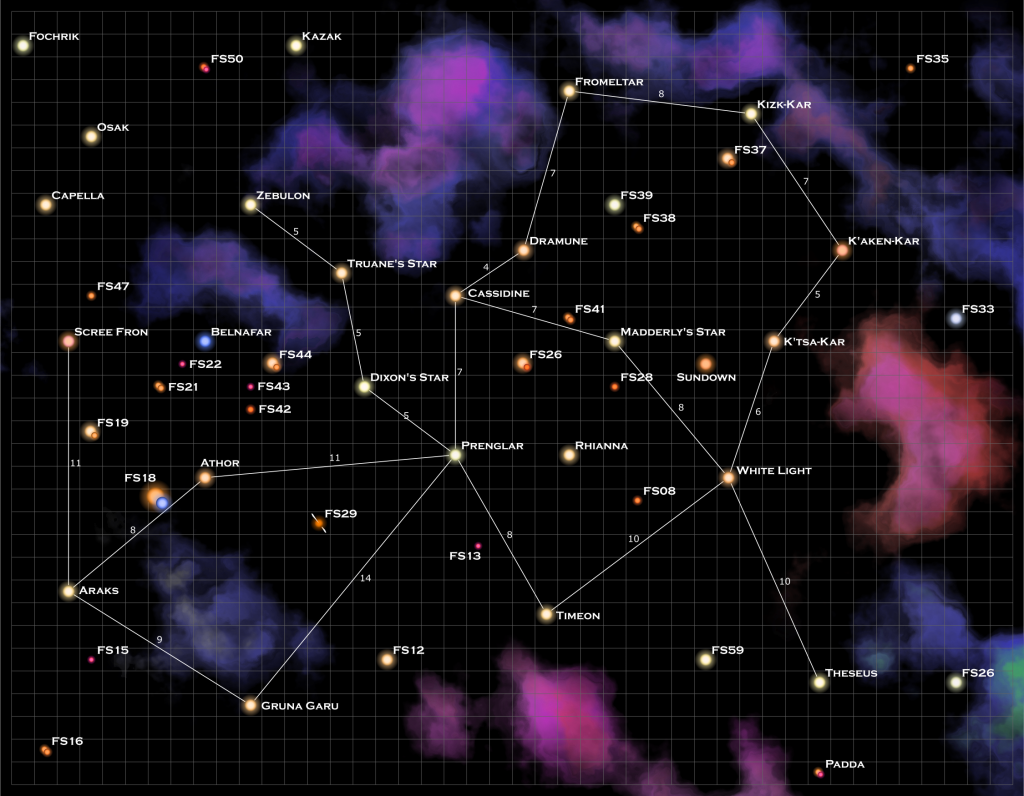
That’s the numbers for a single system. There are 17 inhabited star systems on the AD map (not counting the Zebulon system) for a total of 19 jump routes. If there is a single flight along each route, once a month, you need a starliner for each leg plus a spare. And a shuttle in each system. That’s 55 ships. Of course that ignores the fact that some of the systems have two inhabited worlds (23 in all) and you’ll need more shuttles at those worlds and some ships to move passengers between the two planets in the system.
Now 55 ships (or 67 to account for the two world systems), isn’t too bad, but that is only a single trip every 28 days. If you want a daily trip between systems, you need 30×19 starliners (570 ships) plus 2×17 shuttles for a total of 604 ships. Again, accounting for the two planet systems, that’s another 6-12 shuttles and anywhere from 6 to 168 interplanetary starliners depending on how frequent you make the trips (6 shuttles and 6 ships for once every 28 days and 12 shuttles and 168 ships for daily trips).
With the starship construction centers only capable of supporting about 1500-2300 ships, we’re now looking at about one quarter to one half of the total ship capacity of the Frontier just to connect the worlds for a few hundred people moving between each system each day.
If you want more people moving between the worlds, you have several choices. First, you can make the passenger density higher and make each ship carry more. But that’s only realisticaly a factor of 2 or 3. As another option, you can make the starliners bigger. But remember, if the average ship size increases, the total number of ships the Frontier can support goes down. The final option is to increase the number of ships that the Frontier can support.
Implications
What this all means is that you have to make a decision about interstellar travel. If you have few ships, then trips are few and far between and not a lot of people will be traveling between worlds. Your characters should expect to spend months or years on a single world with all their adventures there, as getting tickets to move between worlds could be relatively rare depending exactly on how you structure it. It also probably means they won’t have their own ship as they are too rare.
Additionally, unless there are daily (or every other day) flights between each world, then it will take a long time to travel across the Frontier with layovers of several days to weeks in each system depending on the frequency and scheduling. If they are traveling between worlds, then there will be even longer spans of time (above the already long base travel times) between adventures and your plots need to account for those long time scales.
This article was focused simply on the logistics of travel and the number of ships it would take to support that. I didn’t even address the costs and economics of each individual flight. That will be part 1b at a future date.
What are your thoughts on the number and size of passenger liners? How do you handle it in your game? What other implications have you thought of that I didn’t cover? Let me know in the comments below.
One thought on “Economics of Spaceflight – part 1a – Starliners”